Connectoria terminalia funguntur ut partes criticae in systematibus electricis, firmandi coniunctiones fidas inter fila, cables, et variarum generum machinas electricas. Haec elementa necessaria adiuvant transitum tutum et efficacem currentis electricae, dum integritatem structuralem servant in condicionibus operationis gravibus. Intellectus factorum quae conferunt altam conductivitatem et robur mechanicum in connectoribus terminalibus est primarius pro ingeniariis, technicis, et procuratoribus qui operantur in variis applicationibus industrialibus.
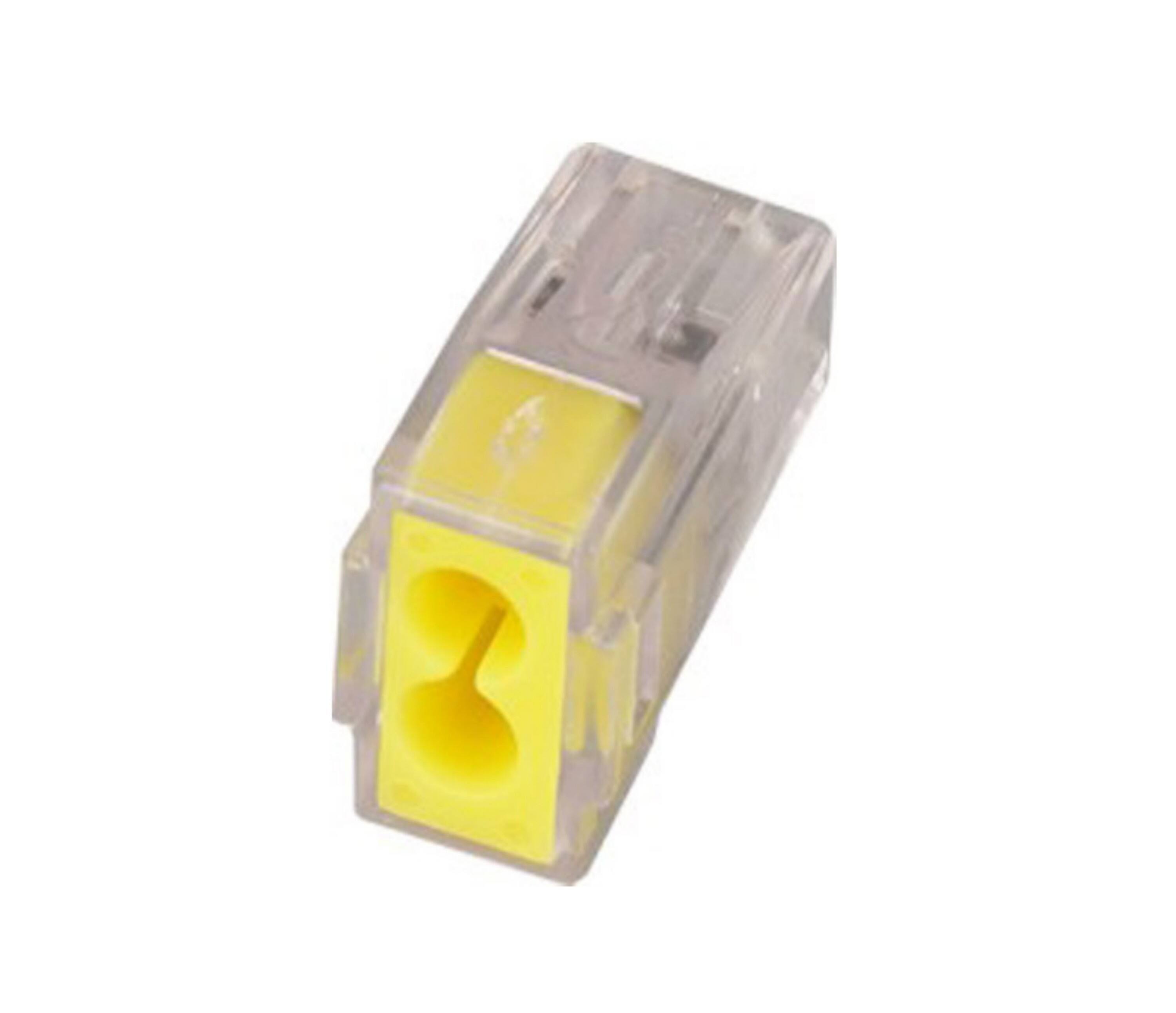

Proprietates functionales connexilorum terminalium directe afficiunt systematis fidem, efficientiam operationalem et longaevam rationem manti. Rationes industriales hodiernae connexiles postulant qui extremas temperaturas, vibrationes, substantias corrosivas et onera electrica ferre possint, interea tamen perficientia constans per longos periodos servatur. Electio connexilorum terminalium idoneorum multas parameters technicas et condiciones ambientales, quae perficientiam tam electricam quam mechanicam influunt, diligenter considerandas requirit.
Selectio Materialium pro Optima Operatione
Materiales Conductivae et Eorum Proprietates
Materiae conductivae quae eliguntur valde influunt in praestantia electrica connectorum terminalis. Aeneum manet materia maxime communiter usata propter excellentiam suam in conductu, resistentia corrosionis, atque proprietatibus mechanicis. Aeneorum legationes altitudine purae praestantiam superiorem gerendi currentis habent, tamen stabilitatem structuralem servantes sub cyclis thermalis. Aeneum argento allatum praestantiam meliorem in conductu et resistentia oxidationis praebet, praesertim utilis in applicationibus altifrequentibus.
Coniunctiones terminalis alliganti presentia costituunt optiones minus pretiosas pro certis usibus, licet habeant diligenter considerari coëfficientes expansionis thermalis et periculum corrosionis galvanicae. Electio inter cuprum et alligantem pendet a factoribus inclusis necessitudinibus currentis, conditionibus environmentalibus, et considerationibus oeconomicis. Alligamenta cuprea specialia, quae continent elementa ut stannum, phosphorum, vel beryllium, augent proprietates speciales sicut qualitates elasticae vel stabilitatem thermalem.
Systemata praetiosorum metallicorum, inter quae aurum, argentum, et platinam, praebent meliorem resistentiam corrosioni et retinent contactum resistentiae infimae per tempus. Haec tegumenta sunt praesertim utilia in applicationibus criticis ubi fiducia coniunctionis non potest compromitti. Spissitudo et qualitas tegimenti afficiunt directe usum diuturnum et efficaciam pretii. conectores terminales in exiguis ambientibus.
Materiae Insulationis et Proprietates Dielectricae
Materiae insultrices circum conectores terminales debent praebere sufficientem vim dielectricam, dum integritas mechanica in stressibus operationum servatur. Materiae thermoplasticae, ut nylon, policarbonas et polyamidum, offerebunt aequationem excellentem inter isolationem electricam et proprietates mechanicam. Haec materiae resistantiam ostendunt ad factores environmentales, ut humor, chemica, et variationes temperaturae.
Plasticae thermosetae stabilitatem thermica et accuratiam dimensionalem augentant comparatae ad alternationes thermoplasticas. Resinae phenolicae, melamin-formaldehydum, et composita epoxica praestant praestationem superiorem in applicationibus altitermicae. Temperatio transitus vitreae et characteristicas expansionis thermalis materiae insultricis impingunt directe in fidem conectoris sub conditionibus cyclandi thermaliter.
Additiva retardanda flammatum servant ad normas tutelarum servandas, simulque proprietatibus electricis retentis. Materialia ad UL ratum habent probatas praestationis classes pro specificis tensionis et currentis ratibus. Electio convenientium materialium insulatorum eget ponderationem inter necessitates electricas, proprietates mechanicæ, resistentiam ambientalem, et normas regulativas pro conectoribus terminalibus.
Factores Designis Affectantes Conductivitatem
Area Superficialis et Geometria Contactus
Area superficialis contactus inter componentes coniungentes directe influat in capacitem ferendam currentis et resistentiam contactus conectorum terminalium. Maior area contactus distribuit onus electricum efficacius, minuitens calefactionem localem et melius totam fidem. Geometria superficiei contactus afficit distributionem pressionis contactus et formationem stabilium conectionum electricarum.
Designationes contactuum multiplex vias currentes praebent, fidem augendo et effectum contaminationis superficialis vel corrosionis localis minuendo. Contactus onerati a molle pressionem constantem servant tempore, expansioni thermicae et depositioni mechanicali compensando. Finis et textura superficialis areae contactus resistentiam contactus initialem et stabilitatem diuturnam coniunctionum electricarum influunt.
Effectus marginis et phaenomena congerie currentis calidas sedes et degradationem acceleratam in coniunctionibus terminalibus male descriptis creare possunt. Geometria contactus recta fluxum currentis aequabiliter distribuit, stressionum localium concentrationes minimizando et vitam operationalem extendendo. Instrumenta designandi auxilio computatrali optimisationem geometriae contactus ad necessitudines electricas et mechanicus specifcas permittunt.
Methodi Terminatio Filorum
Modus terminandi filum valde afficit operationem electricam et fiduciam mechanicam connexilium terminalium. Connexionis compressae pressionem contactus constantem et obsignationes hermeticas praebent, si recte fiant cum instrumentis et technicis idoneis. Figura comprimationis varietates magnitudinis fili capere debet, interea pressionem contactus et levamentum strain sufficientia conservans.
Terminales scalarum formae connexionibus regolabilibus in loco utuntur et varias magnitudines filorum in intervallis specificatis recipiunt. Specifica torque et figura filettorum distributionem pressionis contactus et stabilitatem diuturnam influunt. Nimia constrictio filamenta fili nocere potest vel concentrationes stress creare, dum parum constrictio resistentiam contactus augere et defectum eventualem connexionis causare potest.
Terminales cum cage helicoidali praebent installationem absque instrumento, tamen retinent pressionem contactus constantem per tempus. Mechanismus helicoidalis compensat depositionem fili et expansionem thermicam, securitatem connexionum electricarum stabilium garant. Terminales compressi offerunt facultates installationis rapidas, tamen retinent vim contactus idoneam ad transfertum currentis fidelem in applicationibus connexorum terminalis.
Considerationes de Robore Mecanico
Design Structurale et Distributio Onérum
Design mecanicum connexorum terminalis variis generibus stressis accomodare debet, inclusis oneribus tractivis, compressivis et torsionis. Distributio recta onerum vitat concentrationes stressis quae possent ducere ad defectum praeaturum vel ad deterioratam functionem electricam. Geometria thori et crassitudo materiae directe influunt roborem mechanicum et stabilitatem dimensionalem sub oneribus operationum.
Functio fortificationis, ut costae, domini et sectiones crassiores, integritatem structuralem augent sine materialis usus vel pretii notabiliter augebunt. Rationem aspectūs et crassitudo parietis sedes conectorum afficit vim resistentiae deformationi sub stressibus mechanicis. Analyse finita elementorum permittit optimisationem designum structuralium ad conditiones oneris specificas et factores tute.
Selectio materiae pro componentibus sedium mechanicas proprietates cum electricis necessitatibus et resistentia environmentali aequilibrare debet. Plasticae firmamenta ingeniaria altae firmitudinis praebent excellentes rationes firmitudinis ad pondus simul retinentes proprietates isolationis electricae. Sedes metallicaee protectionem mechanicam superiorem praebent sed curam diligenter habendam de necessitatibus isolationis electricae et terraectionis pro installationibus terminalium conectorum.
Caracteristicae Protectionis Environmentalis
Systemata obsignandi environmentalia componentes internos protegunt contra humorem, pulverem, chemicas et alias contaminantes quae praestantiam imminuere vel defectum praematurum causare possent. Gradus protectionis IP determinant altitudinem protectionis contra introitum materiae alienae. Materiae cuniculorum et superficies obsignantibus integritatem servare debent sub temperiei mutatione et stressu mechanico.
Coatinga et tractationes resistentes corrosioni vitam operativam producunt in environmentis asperis. Anodizatio, chromate conversion coatings et finishes organicae protectionem barrierae praebent contra substantias corrosivas. Compatibilitas inter diversa materialia corrosionem galvanicam prohibet quae integritatem mechanicam et praestantiam electricam connexilium terminalis compromittere potest.
Functiones relaxationis strain protegunt coniunctiones filorum a damno mechanico propter vibrationem, flexionem vel tensiones installationis. Recta ratio cablorum minuit tensiones in punctis terminationis et prolongat vitam cabli. Designus locorum introitus et ductus cablorum afficit tam protectionem mechanicam quam operationem electricam in systematibus installatis.
Qualitas Controlis et Normae Experientiae
Examinatio Electrica Praestantiae
Testus electricus comprehensivus verificat characteristicas functionum connexilorum terminalis sub conditionibus operationis specificatis. Mensurationes resistentiae contactuum certificant rectam continuitatem electricam et identificant problemata potentiaria coniunctionis antequam installentur. Testus capacitas ferendi currentis probant performantiam thermalem et margines tutionis sub conditionibus oneris maximi.
Testis firmitatis dielectrici inspiciet integritatem isolationis et marge tutelae pro certis tensionibus. Testis altior potentialis defectus in isolatione detegit, qui ad disruptionem electricam vel pericula tutelae ducere possent. Testis impulsi tensionis conditiones transitoriae supra tensionis simulant, quae in applicationibus realibus eveniunt.
Testis accessionis calorifici sub currentibus nominalibus praestantiam thermalem inspicit, ut regulis tutelae et descriptionibus technicis satisfiat. Testes cyclorum thermalium stabilitatem praestantiae sub variationibus temperature repetitis evaluant. Testes senescentiae prolongatae velocitates degradationis aestimant et vitae operativae terminalium coniunctionum in conditionibus usus exspectationem praedictant.
Assessio Durabilitatis Mechanicae
Protocolli experimentorum mechanicorum vim structuralem et constantiam dimensionalem sub variis conditionibus oneris evaluant. Experimenta vis trahendi verificant retentionem fili et securitatem coniunctionis. Mensurae virium inserendi certum faciunt aptationem debitem et processus installationis usui accommodatos.
Experimenta vibrationis conditiones operationales simulantes modos defectus potestiales quae ad strepitum mechanicum pertinent detegunt. Experimenta ictus resistentiam ad onera impulsiuaria et strepitus transportis evaluant. Experimenta oneris cyclica resistentiam ad fatigationem et fidem mechanicam diuturnam connexilorum terminalium sub stressibus repetitis assequuntur.
Experimenta environmentalia, inter quae variationes temperatura, expositionem humidi et verificationem resistentiae chemicis, fiendam certam sub conditionibus usus praestant. Experimenta pulverizationis salinae resistentiam corrosioni et firmitatem tegmentationum evaluant. Experimenta expositionis UV degradationem componentium plasticorum sub expositione solis in usibus externis aestimant.
Optimae Practicae Installationis
Technicae Installationis Rectae
Rectae installationis procedurae magnopere influunt in praestationem et fidem coniunctionum terminalium per totam vitae operationalem. Preparatio fili, inclusa iusta strippationis longitudine, munditia conductoris et ordinatio filamentorum, contactum electricum optimum efficit. Usus instrumentorum idoneorum et specificatorum torque impediat damnum durante installatione dum securitatem coniunctionis idoneam firmat.
Considerationes environmentalis durante installatione longam praestationem et fidem afficiunt. Humectio regula, contaminatio preventa et rectae procedure sigillandi coniunctiones a factoribus degradationis protegunt. Conditiones temperaturaeduring installationem proprietates materialis et integritatem coniunctionis afficere possunt, praesertim pro componentibus thermoplasticis.
Documenta et verificationis procedurae garantunt rectam installationem et futuras operationes conservationis faciliant. Mappae connectionis, acta torsi, et experimenta verificationis praestant data fundamentales ad systematis observationem continuandam. Recta appellationes et systemata identitatis operationes conservationis et quaestionum solutionem efficientem pro installationibus conectorum terminalium adiuvant.
Requisita de Manutenentia et Cautela
Inspectionis et conservationis more solenni tempore regulari augent vitam operationalem et defectum praematurum conectorum terminalium prohibent. Inspectione visualem signa hyperthermiae, corrosionis, vel damni mechanicorum, quae praestationem minuere possent, agnoscunt. Monitoring thermographicum anomalias caloris detegit quae problemata connectionis crescentia indicant.
Rationalem experimentum electricum temporiense probat operationem intra limites specificatos. Mensura contactus resistentiae degenerationis signa detegit antequam ad critica nivea perveniunt. Experimentum resistentiae isolationis securitatem electricam servat et conditiones defecti terrae prohibet quae instrumenta coniuncta nocere possent.
Schemata mantentionis preventivae debent conditiones ambientales, onerum factores et necessitates systematis criticas ratione habere. Maius inspectarum intervalla fortasse necesse sunt in ambientibus asperis vel in applicationibus criticis. Criterium substitutionis super mensuris operationis et aestimatione conditionis visualis dependens operationem firmam praestat, dum mantentionis sumptibus pro systematibus coniunctorum terminalium optime aguntur.
FAQ
Quae materiae optime conducunt pro coniunctoribus terminalibus?
Aeris et lega aerisi optimalis combinationem conductivitatis electricae, proprietatum mechanicarum, et sumptuosa efficacia pro applicationibus plerum conectorum offerunt. Argentum conductivitatem altiorem praebet, sed sumptu maior fit, idque applicationibus criticus vel alti frequentionis aptum reddit. Aurum in aerisi substratis combinat excellentem conductivitatem cum superioribus proprietatibus contra corrosionem ad fidem diuturnam.
Quomodo pressio contactus effectit in praestantia conectoris terminalis?
Pressio contactus satis est essentialis ad resistentiam contactus bassam et fidam coniunctionem electricam in conectoribus terminalibus. Pressio insufficiens in resistentia crescente, cale, et potentiali coniunctionis defectum resultat. Pressio nimis potens conductoribus nocere vel stress concentrationes creare potest. Ratione propria pressionem constantem in limitibus optimalibus per totam thermarum operationalem range certum facit.
Quae sunt conditiones environmentalis quae maxime saepe fidem conectoris terminalis afficiunt?
Mutationes temperaturae, humiditas et vibrationes praecipua pericula environmentalia pro connexibus terminalibus sunt. Mutationes temperaturae dilationem et contractionem thermalem causant, quae coniunctiones laxare aut tensiones augere possunt. Humiditas intrans corrosionem promovet et vim insulationis minuit. Vibrationes mechanicae corrosionem per fricationem et lentam connexiorum relaxationem tempore causare possunt.
Quomodo idoneam quantitatem currentis electricae pro connexibus terminalibus determinare possum?
Quantitates currentis electricae pro connexibus terminalibus in magnitudine conductoris, area contactus, facultate dissipandi calorem et conditionibus temperaturae ambientis dependebunt. Specificata a fabricante praebebit quantitates fundamentales sub conditionibus normalibus. Factores reductionis adhibendi sunt pro altioribus temperature, locis conclusis vel connexibus aggregatis. Limes tuitivus operationem firmam sub pessimis conditionibus praestat simulque oburationem aut defectum celerem vitat.
Index Rerum
- Selectio Materialium pro Optima Operatione
- Factores Designis Affectantes Conductivitatem
- Considerationes de Robore Mecanico
- Qualitas Controlis et Normae Experientiae
- Optimae Practicae Installationis
-
FAQ
- Quae materiae optime conducunt pro coniunctoribus terminalibus?
- Quomodo pressio contactus effectit in praestantia conectoris terminalis?
- Quae sunt conditiones environmentalis quae maxime saepe fidem conectoris terminalis afficiunt?
- Quomodo idoneam quantitatem currentis electricae pro connexibus terminalibus determinare possum?